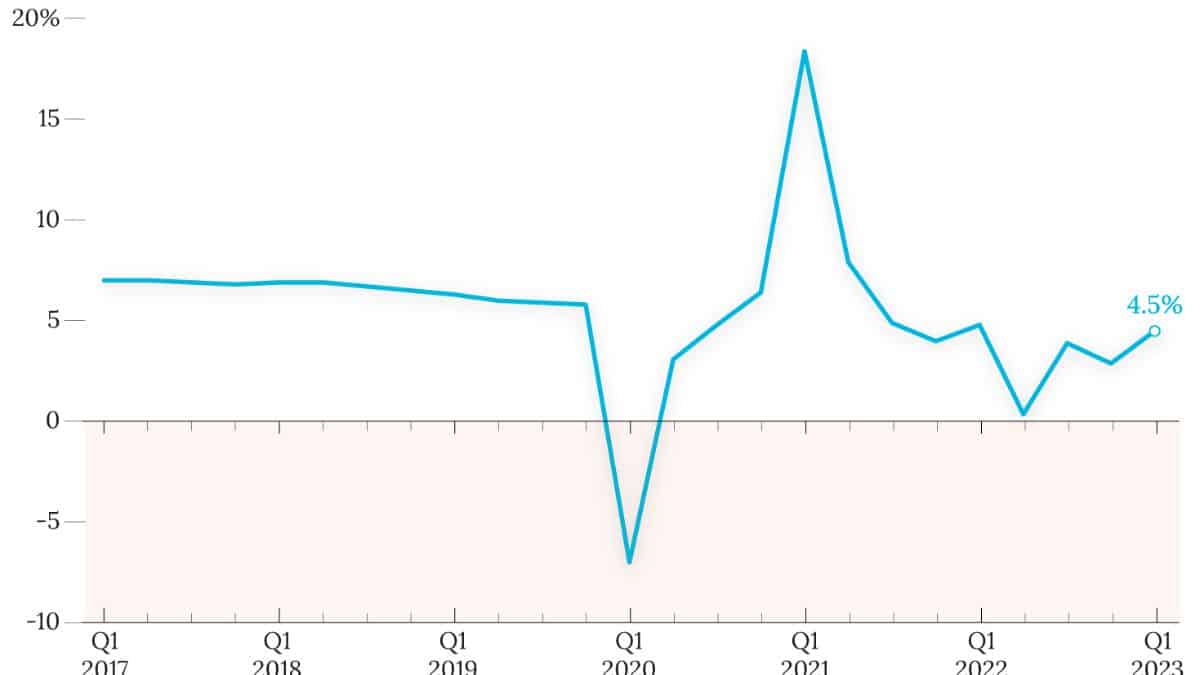
According to the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), China’s economy showed resilience in the first half of 2024, with GDP growing by 5% to reach 61.68 trillion yuan ($8.49 trillion). This growth underscores the continued momentum of the world’s second-largest economy as it emerges from the pandemic-induced slowdown.
A key factor contributing to this growth has been the continuous improvement in overseas demand. China’s export sector has seen a robust recovery, driven by the global economic rebound and increased demand for Chinese goods. The manufacturing sector, in particular, has benefited from strong foreign orders, which have helped to offset some of the domestic economic challenges.
Domestically, there has been a noticeable pick-up in consumer spending. The government’s efforts to boost domestic consumption have started to bear fruit, with retail sales showing significant improvement. Initiatives such as subsidies, tax incentives, and support for small and medium-sized enterprises have helped to enhance consumer confidence and spending power. Additionally, the lifting of COVID-19 restrictions has facilitated a return to normalcy, encouraging people to spend more on services and entertainment.
The Chinese government has also played a pivotal role in sustaining economic growth through proactive policy support. Various fiscal and monetary measures have been implemented to stabilize the economy and promote growth. Infrastructure investment has remained a critical component of this strategy, with significant spending directed towards the development of transportation, energy, and digital infrastructure.
Moreover, targeted support for key industries and sectors has been instrumental in driving growth. The technology and innovation sectors, for example, have received substantial backing, aligning with China’s broader goals of technological self-sufficiency and global competitiveness. Measures to enhance research and development, alongside incentives for high-tech industries, have spurred advancements and attracted both domestic and foreign investments.
Despite these positive developments, challenges remain. The global economic environment is still uncertain, with ongoing geopolitical tensions and potential trade disruptions posing risks. Additionally, domestic issues such as high debt levels and demographic changes require careful management to ensure sustainable growth.